
Residential Wind Turbines : the key to efficient operation – maintenance
As a clean and renewable energy source, Residential Wind Turbines has been widely used around the world. However, as a large mechanical equipment, wind turbines

As a clean and renewable energy source, Residential Wind Turbines has been widely used around the world. However, as a large mechanical equipment, wind turbines

As a clean and renewable energy source, Wind Power Generator has developed rapidly in recent years. However, the applicability of wind turbines is not the

Wind Turbine Generator, as a clean and renewable energy source, has developed rapidly around the world in recent years. The power generation capacity of wind

Micro Wind Turbine, as an environmentally friendly and energy-saving source of electricity, have gradually attracted people’s attention in recent years. Compared with large wind turbines,

Micro Wind Turbine: Are they worth investing in? In recent years, with the rise of renewable energy, Micro Wind Turbine have gradually come into people’s view.

As people’s pursuit of clean energy becomes increasingly strong, home wind turbines are gradually coming into the public eye. However, many people still have some

Introduction In the context of the global energy transition, wind turbines and solar energy are two major clean energy technologies that are gaining increasing attention.

Wind turbine inverters: exploring feasibility and potential Wind turbines play a vital role in the renewable energy sector, with a focus on improving power generation

The Importance of Wind Turbine Inverters Wind power is crucial for the future energy landscape and relies on inverters as a key component. The selection

The function and principle of wind and solar hybrid controller Optimize Renewable Energy Integration with our Wind-Solar Hybrid Controller | Ensure Grid Stability & Enhanced
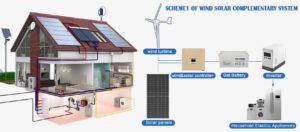
1、What is a hybrid wind and solar system? A solar-wind hybrid system combines solar power generation and wind power generation, two renewable energy technologies, to

The relationship between the number of blades and power generation efficiency The number of blades of a wind turbine is one of the key factors